Como o kit de cateter venoso central atinge fins médicos através da sinergia de vários componentes?
Análise dos componentes principais do kit
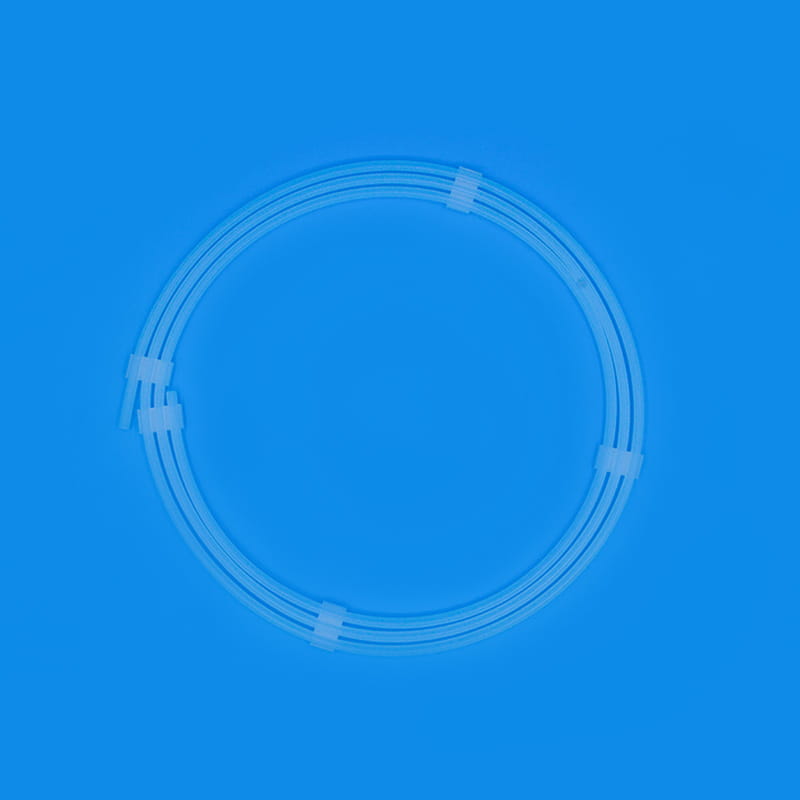
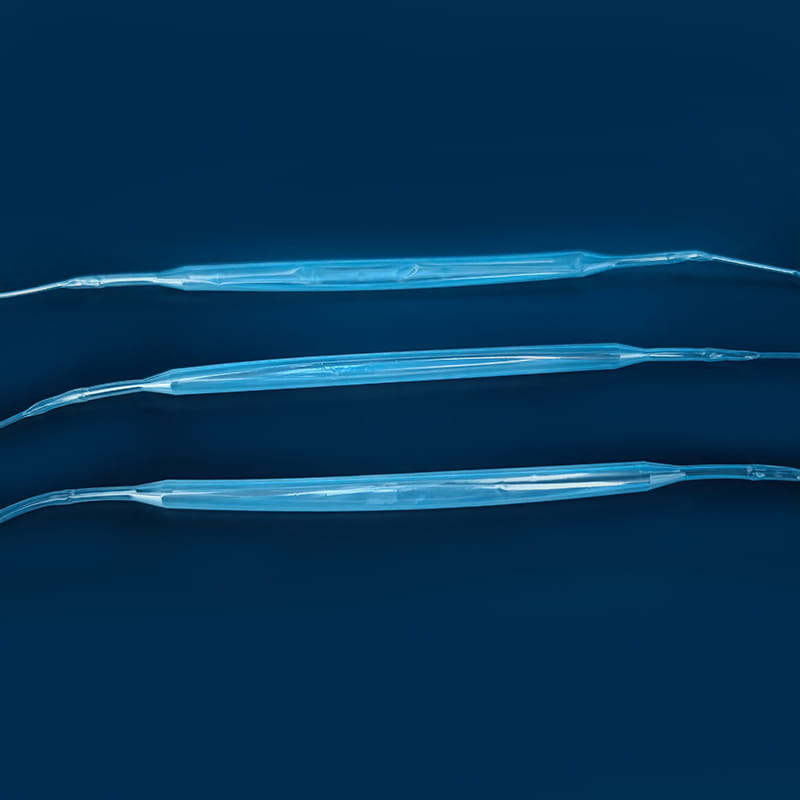
O kit de cateter venoso central Contém uma variedade de componentes -chave, cada um dos quais desempenha um papel único e insubstituível em todo o processo de operação médica. O primeiro é o cateter venoso central, que é o componente central do kit e é o canal que conecta a veia central fora do corpo e dentro do corpo. Seu material é geralmente feito de poliuretano ou silicone de nível médico. Tais materiais têm boa biocompatibilidade e podem reduzir efetivamente a rejeição do corpo por corpos estranhos e reduzir o risco de complicações como a infecção. Diferentes tipos de cateteres venosos centrais têm suas próprias características em estrutura e função. Os cateteres de lúmen única são adequados para necessidades de tratamento único, enquanto os cateteres de dupla lúmica ou multi-lúmen podem realizar uma variedade de operações médicas diferentes ao mesmo tempo, como infusão, coleta de sangue e administração de medicamentos, o que melhora muito a eficiência e a conveniência das operações médicas. Em termos de design, algumas superfícies de cateter são tratadas com revestimentos especiais para melhorar ainda mais as propriedades anti-trombóticas; Alguns também são marcados com escalas para facilitar a equipe médica para entender com precisão a profundidade da inserção.
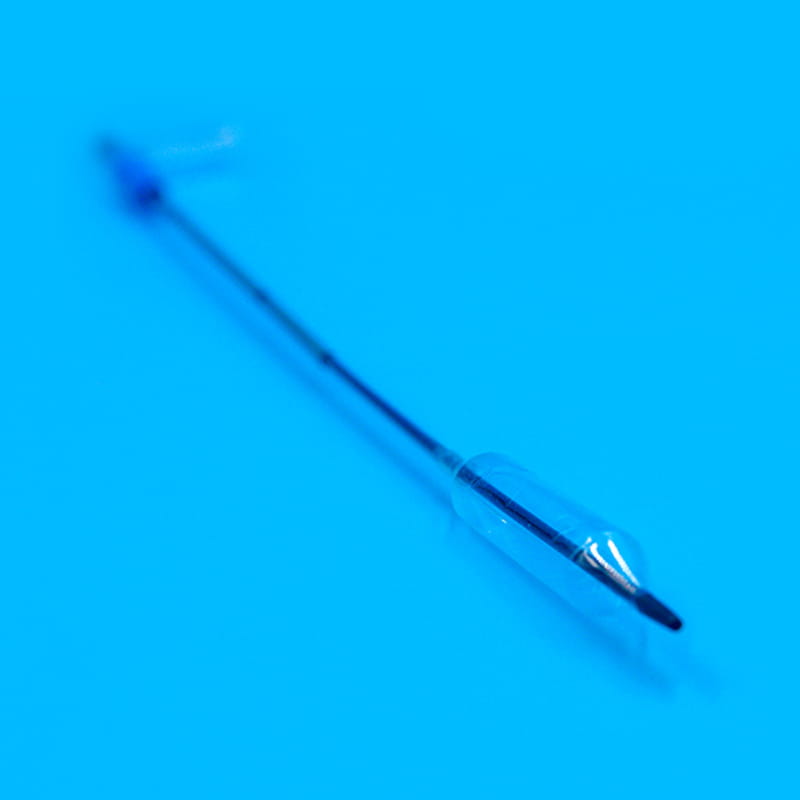
O cannula plays a pioneering role in the central venous catheter kit. When performing a central venous catheter insertion operation, the cannula is first used for percutaneous puncture into the vein. Its needle tip adopts a bevel cutting process. This design is sharp and precise, and can quickly and accurately penetrate the skin and vein wall with minimal resistance, opening a channel for the entry of subsequent components. The needle core and outer sleeve of the cannula needle are closely matched. When the cannula needle successfully enters the vein, the inner needle core is removed through a special separation mechanism, and the outer sleeve with a certain hardness and flexibility will remain in the vein as a guide channel for subsequent guide wires and other components to enter. To ensure the accuracy of puncture, some cannula needles are also equipped with ultrasound guidance adapters, which can be used with ultrasound equipment to observe the puncture path and blood vessel status in real time.
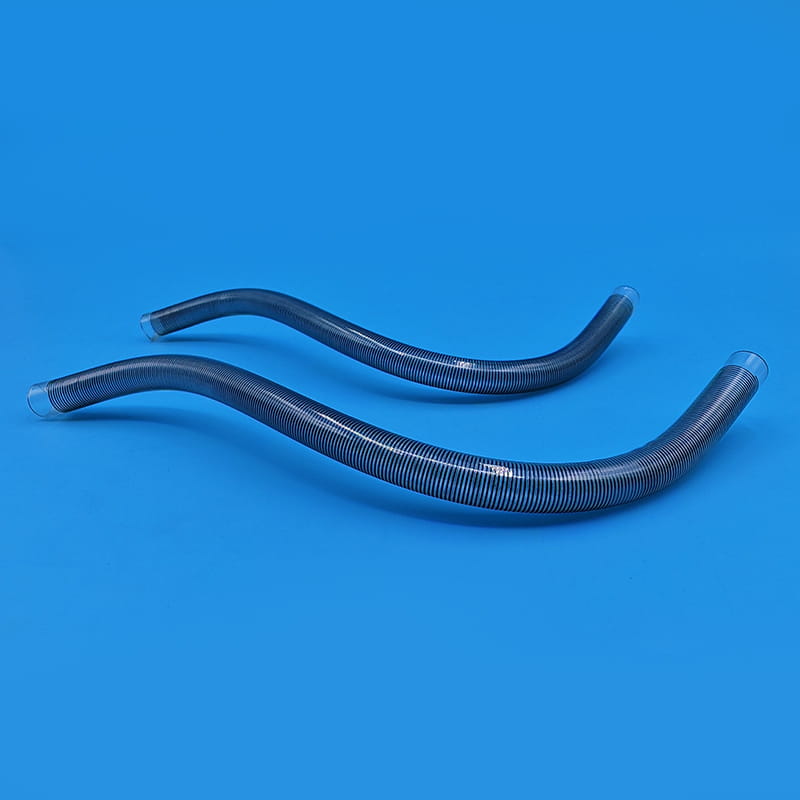
O guidewire is a key tool for precise positioning and guidance in the central venous catheter kit. After the cannula needle establishes the initial channel, the guidewire will be sent into the vein through the cannula. The outer layer of the guidewire is usually woven from medical-grade stainless steel wire, and the inner layer is a nickel-titanium alloy core. This structure gives the guidewire good flexibility and maneuverability. Doctors can use the J-shaped or straight head design of the guidewire tip to flexibly turn and guide it in the blood vessel through in vitro operation, and accurately send it to the target position. Some high-end guidewires also have a hydrophilic coating, which becomes lubricated after contact with blood, further reducing friction damage to the inner wall of the blood vessel. The existence of the guidewire makes the insertion path of the central venous catheter clearer and more controllable, laying a solid foundation for the smooth insertion of the subsequent catheter.
O role of the dilator in the central venous catheter kit should not be ignored. Since the diameter of the vein is relatively thin, and the central venous catheter needs to be smoothly inserted, it is necessary to properly dilate the vein. The dilator usually adopts a conical or cylindrical design, and the material is mostly medical-grade polyethylene. It can enter the vein along the guidewire and expand the channel of the venous puncture site by gradually expanding. During the expansion process, the smooth surface treatment and gradual caliber design of the dilator can reduce damage to the venous tissue while ensuring effective expansion. For special patients, such as those with thin blood vessel walls or sclerosis, there are also special controllable dilators available, and doctors can accurately adjust the expansion strength and range according to actual conditions.
O peelable sheath is an important part of the central venous catheter kit to ensure the safe insertion of the catheter. After the dilator completes the dilation of the vein, the peelable sheath will be sent into the vein along the guidewire and dilator. The peelable sheath consists of two symmetrical half sheaths connected by a special locking structure in the middle. When the peelable sheath reaches the appropriate position, the central venous catheter will be inserted into the vein through the sheath. At this time, the medical staff will separate the peelable sheath from the middle lock and remove it from the body through a specific operation technique, while the central venous catheter will be left in the vein. This unique design not only ensures the smooth catheter insertion process, but also avoids unnecessary damage to the vein and catheter. To prevent accidental scratches on the surrounding tissue when the sheath is peeled off, the edge of the sheath is specially rounded and blunted.
O fixing device plays a role in stabilizing and fixing the catheter in the central venous catheter kit. In order to ensure that the central venous catheter can maintain a stable position in the patient's body for a long time without displacement or falling off, fixing devices such as sutures, sterile dressings or special catheter fixers will be used to fix the catheter to the patient's skin. The suture fixation method is suitable for patients with long-term catheterization. The catheter is fixed to the skin tissue through delicate suturing operations; the sterile dressing is breathable, waterproof and antibacterial, and can effectively protect the puncture site; the dedicated catheter fixator is made of medical-grade silicone or polymer materials, and can be personalized according to the patient's skin morphology and catheter model through an adjustable buckle design. Appropriate fixation can not only ensure the normal function of the catheter, but also reduce the discomfort and potential risks caused to the patient by the movement of the catheter.
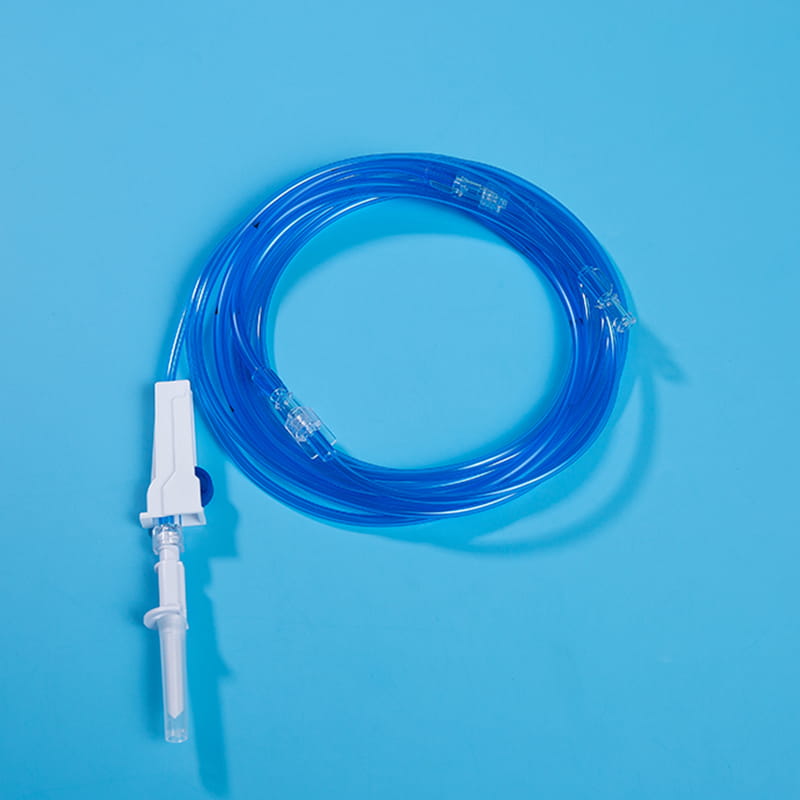
O interface for external connection is the bridge between the central venous catheter and external medical equipment. Through these interfaces, the central venous catheter can be connected to infusion sets, syringes and other equipment to achieve various medical operations such as infusion, drug administration, and blood collection. The design of these interfaces has good sealing and compatibility, and common ones include Luer connectors and needleless infusion connectors. The Luer connector is connected by threads to ensure a tight connection without leakage; the needleless infusion connector adopts a diaphragm design, which can complete the infusion operation without acupuncture, reducing the risk of infection. At the same time, some interfaces also have anti-backflow function to prevent blood from reflux and blocking the catheter, and support multiple devices to be connected at the same time to meet complex clinical needs.
Ampla gama de cenários de aplicação clínicos
Em aplicações médicas reais, os cenários de uso de kits centrais de cateter venosos são muito amplos. No campo de terapia intensiva, para pacientes com condições críticas que precisam de uma grande quantidade de infusão e medicamentos frequentes, os cateteres venosos centrais podem fornecer um canal de infusão rápido e estável para atender às necessidades dos pacientes de fluidos e medicamentos. Tomar pacientes com choque séptico como exemplo, durante o processo de resgate, uma grande quantidade de líquido cristalóide, líquido colóide e medicamentos vasoativos precisam ser complementados em um curto período de tempo. O cateter venoso central pode garantir que esses fluidos e drogas entrem rapidamente na circulação sanguínea e corrigem rapidamente o estado de choque. Ao mesmo tempo, o monitoramento hemodinâmico também pode ser realizado através do cateter venoso central. O médico conecta o sensor de pressão à interface do cateter para obter parâmetros como pressão venosa central e pressão de cunha da artéria pulmonar em tempo real, o que ajuda os médicos a entender a função cardíaca do paciente e o status de circulação sanguínea em tempo real e fornece uma base importante para a formulação de planos de tratamento precisos.
No tratamento tumoral, muitos medicamentos quimioterapia são altamente irritantes para os vasos sanguíneos, e a administração através de veias periféricas pode causar complicações como flebitis. O kit de cateter venoso central pode colocar um cateter na veia central, permitindo que os medicamentos quimioterápicos entrem diretamente nos grandes vasos sanguíneos e sejam rapidamente diluídos, reduzindo assim a irritação nos vasos sanguíneos, reduzindo a probabilidade de complicações e melhorando a tolerância ao tratamento dos pacientes. Por exemplo, pacientes com câncer de mama que recebem medicamentos quimioterápicos altamente irritantes, como a doxorrubicina, podem usar cateteres venosos centrais para evitar efetivamente consequências graves, como necrose da pele e ulceração de tecidos causados pelo extravasamento de medicamentos. Ao mesmo tempo, para pacientes que precisam de quimioterapia a longo prazo e múltipla, os cateteres venosos centrais reduzem a dor de perfurações repetidas e melhoram a continuidade do tratamento.
Além disso, na terapia de apoio nutricional, os cateteres venosos centrais podem ser usados para o apoio total da nutrição parenteral total a pacientes que não podem receber nutrição suficiente através do trato gastrointestinal, como pacientes com coma de longo prazo e queimaduras graves. Dar solução de nutrientes de alta concentração e alta caloria através da veia central pode atender às necessidades do corpo do paciente de nutrientes e promover a recuperação do paciente. Tomando pacientes com queimaduras extensas como exemplo, sua função gastrointestinal é suprimida devido a trauma e eles não podem digerir e absorver alimentos normalmente. Nesse momento, a solução nutriente all-in-one contendo aminoácidos, emulsão de gordura, glicose e outros ingredientes é dada através do cateter venoso central para manter o equilíbrio de nitrogênio do paciente, reabastecer a energia exigida pelo corpo e acelerar a cicatrização de feridas. Ao mesmo tempo, a equipe médica também pode monitorar os eletrólitos do paciente, o açúcar no sangue e outros indicadores através do cateter venoso central e ajustar o plano de apoio nutricional no tempo.
Procedimentos operacionais rigorosos e padronizados
O operating procedures of the central venous catheter kit need to strictly follow the specifications and standards. Before the operation, the doctor needs to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition, including the patient's age, weight, underlying diseases, coagulation function, etc., and select the appropriate puncture site and central venous catheter type. Common puncture sites include the internal jugular vein, subclavian vein and femoral vein. Different sites have their own advantages and disadvantages, and they need to be carefully selected according to the specific situation of the patient. At the same time, detailed explanations and communication should be given to the patient, and the patient should be informed of the operation process, possible risks and key points of cooperation to obtain the patient's cooperation. During the operation, the principle of aseptic operation must be strictly followed. The puncture site must be disinfected with iodine more than three times, and the diameter of the disinfection range must not be less than 15 cm. A large sterile sheet must be laid to ensure that the entire operation is carried out in a sterile environment. Then follow the steps of trocar puncture, guide wire insertion, dilation with a dilator, insertion of a removable sheath, insertion of a central venous catheter, fixation of the catheter, and connection of an external interface. Taking internal jugular vein puncture as an example, under ultrasound guidance, after determining the puncture point, the trocar is inserted at an angle of 30-45 degrees. After seeing the blood return, it is confirmed that it is in the vein, and then the subsequent components are inserted according to the process. After the operation is completed, the patient needs to be closely observed and cared for, and the patient must be monitored for complications and treated in a timely manner. This includes observing whether the puncture site is red, swollen, or exuded, and changing the dressing regularly; monitoring the patient's body temperature, blood routine, and other indicators to determine whether an infection has occurred; evaluating the function of the catheter to ensure smooth infusion, blood collection, and other operations.
Desafios e riscos enfrentados
Embora os kits de cateter venoso central tenham um papel importante na área médica, eles também enfrentam alguns desafios e riscos durante o uso. A infecção é uma das complicações mais comuns dos cateteres venosos centrais. Como o cateter é deixado no corpo por um longo tempo, é fácil para as bactérias e outros microorganismos invadirem, causando infecção local ou infecção sistêmica. As bactérias entram principalmente no corpo através da colonização da pele no local da punção, contaminação do conector do cateter e contaminação do sistema de infusão. A trombose também é um problema que não pode ser ignorado. O cateter pode estimular o endotélio vascular no vaso sanguíneo, causando alterações na coagulação do sangue, formando um trombo. Uma vez que o trombo caia, pode causar complicações graves, como embolia pulmonar. Além disso, problemas como bloqueio e deslocamento do cateter também podem afetar o uso normal e o efeito do tratamento do cateter venoso central. O bloqueio do cateter pode ser causado pela deposição de drogas, coagulação do sangue, etc.; O deslocamento do cateter pode estar relacionado a fatores como atividade inadequada do paciente e fixação frouxa.
For more information, please call us at +86-18913710126 or email us at .
Os procedimentos intervencionistas vasculares são essenciais para a medicina cardiovascular moder...
Introdução Tubo endobrônquico de lúmen único Os s são um componente c...
Na medicina moderna, os cateteres médicos são ferramentas indispensáveis utilizadas em uma ampl...
Na indústria da saúde, a importância de selecionar os materiais certos para dispositivos médicos ...
Na era da medicina de precisão, um pequeno tubo muitas vezes carrega o peso das responsabilidades...
Nos cuidados de saúde modernos, a gestão precisa de fluidos é crucial para a segurança do pacient...